
leowolfert - Fotolia
The difference between AES and DES encryption
Choosing to encrypt confidential data with AES or DES encryption is an important cybersecurity matter. Learn about the important differences between AES and DES.
Data Encryption Standard and Advanced Encryption Standard sound similar, and both are examples of symmetric block ciphers. That is where the similarities end, however. DES is an outdated method of data encryption, and development on AES began in the late 1990s when DES was deemed inadequate from a cybersecurity standpoint.
When it was initially developed, the DES symmetric-key algorithm was commonly used for data encryption. It was superseded by the more secure AES algorithm when AES became a federal government standard in 2002.
What is DES encryption?
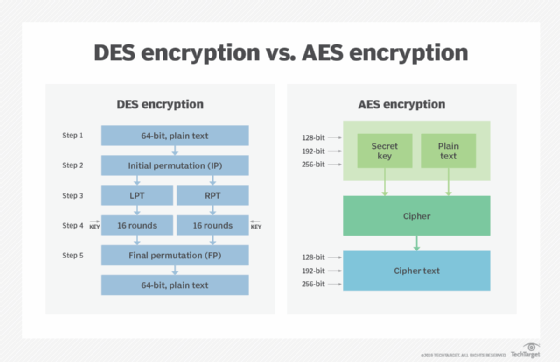
DES is a block cipher, meaning, rather than encrypting one bit at a time, a cryptographic key and algorithm encrypt a block of data concurrently. When using DES, the same private key is used to encrypt and decrypt a message.
DES groups a plaintext message into 64-bit blocks during encryption. Blocks are coded with the key into a 64-bit ciphertext using permutation and substitution. The process, which entails 16 steps and can run in four different modes, either encrypts blocks individually or makes each cipher block dependent on all the previous blocks. The DES decryption process is the inverse of its encryption steps, reversing the order in which the keys are applied.
What is AES encryption?
NIST started developing AES in 1997 when it was discovered that DES was vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Like DES, AES is a symmetric block cipher. In 2001, the U.S. government chose to use AES to protect classified information. It is implemented in software and hardware globally to encrypt sensitive data.
When announcing the development of AES, NIST representatives noted that the advanced encryption algorithm would be unclassified and "capable of protecting sensitive government information well into the next century." AES was intended to offer defense against a variety of attack techniques. It was also designed to be easy to use in hardware, software and restricted environments, such as smart cards.
The key differences between AES vs. DES
There is an important difference when comparing AES vs. DES encryption and decryption algorithms: AES is secure, while DES is not.
The federal government developed DES algorithms more than 40 years ago to provide cryptographic security for all government communications. The idea was to ensure government systems all used the same, secure standard to facilitate interconnectivity. DES served as the cornerstone of government cryptography for more than two decades, but in 1999, researchers broke the algorithm's 56-bit key using a distributed computer system. DES is still used for backward compatibility in some instances, but modern computer systems should not rely on DES for data confidentiality.
AES is a more mathematically efficient and elegant cryptographic algorithm, but its main strength rests in its key length options. The time required to crack an encryption algorithm is directly related to the length of the key used to secure the communication. AES allows you to choose a 128-bit, 192-bit or 256-bit key, making it exponentially stronger than the 56-bit key of DES. Encryption is also much faster in AES vs. DES, making it ideal for applications, firmware and hardware that require low latency or high throughput.







