What are the most common digital authentication methods?
How an organization authenticates users and devices is a hugely important piece in the cybersecurity puzzle. Get to know the various forms of digital authentication.
Digital authentication is the process of verifying that users or devices are who or what they claim to be in order to enable access to sensitive applications, data and services. There are multiple ways to verify authenticity. Here's an outline of the most popular digital authentication methods in the enterprise today.
Unique passwords
When most of us think of authentication, what typically comes to mind is a unique combination of username and password. In the enterprise, passwords remain the most common digital authentication method. Users or devices typically have their own username that is not secret. This username is combined with a unique and secret password known only by the users or devices to access company data, applications and services. While the unique password authentication method works, the number of passwords users must manage can make this approach burdensome. This is one reason why technologies such as single sign-on (SSO) have become so popular. With SSO, a single password will authenticate users and enable access to multiple assigned corporate services.
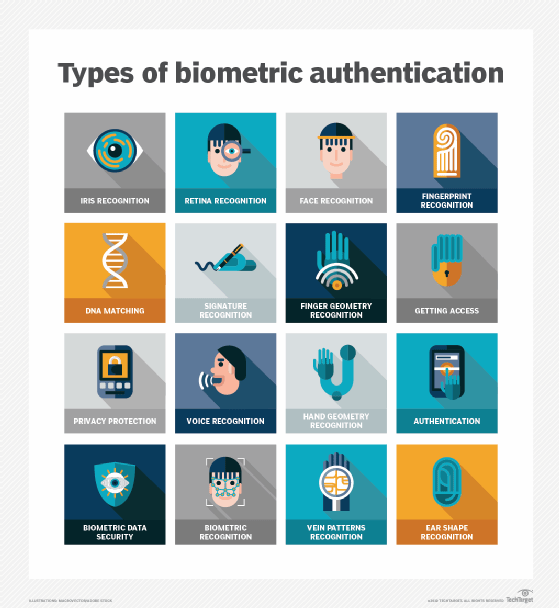
Biometric authentication
It has become common for devices such as smartphones, tablets and PCs to incorporate biometric technologies into their hardware for digital authentication purposes. Fingerprints and facial recognition are used most often; other biometric methods include hand geometry, retina and iris scans, voice recognition and signature-based analysis. While popular, biometrics raises privacy and security concerns that a business will need to work through. It's important to know both the pros and cons of biometric authentication.
Multifactor authentication (MFA)
With multifactor authentication, users verify their identity using two or more methods. A commonly used form of MFA is two-factor authentication (2FA), which takes the standard process of requesting a username and password and applies a second layer of verification. This second layer in 2FA might include a text message sent to a specific mobile phone number, the use of hardware and software tokens, biometric authentication or push notifications to the user.
Adaptive authentication
This approach, which is related to risk-based authentication, enables a security team to set authentication policies to grant or deny access based on a long list of factors, including IP address, user role, location, device, sensitivity of the data being accessed and other risk factors. These context-based elements of adaptive authentication are the basis of the zero-trust model. With a zero-trust strategy, an organization sets its user and device authentication to strict minimums so that, as the name indicates, identity and access management systems trust no one by default. This rejection of the implicit trust concept requires a rigorous, almost continuous authentication -- in contrast to a one-time check at the security perimeter.
Behavioral authentication
Behavioral biometric authentication can involve analyzing keystroke dynamics or mouse-use characteristics. To verify a user or machine, AI analyzes user data or a device's typical computing behavior. If that behavior veers outside predefined baselines, it triggers a lockdown of what that user or device is authorized to access.
Device recognition
Endpoint security management platforms can recognize authorized hardware and immediately enable their access to certain network resources. This type of authentication is especially important for companies that allow users to access business applications on personal devices. It is an added precaution to ensure that only devices deemed appropriate can connect to the network.
Editor's note: This article was originally published in 2020 and has been updated to add new information on authentication technology.
Andrew Froehlich is founder of InfraMomentum, an enterprise IT research and analyst firm, and president of West Gate Networks, an IT consulting company. He has been involved in enterprise IT for more than 20 years.








