Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
What is the Extensible Authentication Protocol?
The Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is a protocol for wireless networks that expands the authentication methods used by the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), a protocol often used when connecting a computer to the internet. EAP is used on encrypted networks to provide a secure way to send identifying information to provide network authentication. It supports various authentication methods, including as token cards, smart cards, certificates, one-time passwords and public key encryption.
EAP methods protect a specific portal so that only users with an authentication key or password can get network access. These methods limit the number of users and help prevent network congestion, making networks faster and more secure. Organizations can use EAP methods to adapt to specific privacy needs and company guidelines.
Extensibility is a key trait of the EAP framework. Some main features of the protocol include the following:
- It provides the framework within which the various authentication methods work.
- It adapts to future security needs.
- It can be kept simple if that's what is wanted.
How does EAP work?
EAP uses the 802.1x standard as its authentication mechanism over a local area network or a wireless LAN (WLAN). There are three primary components of 802.1X authentication:
- the user's wireless device;
- the wireless access point (AP) or authenticator; and
- the authentication database or the authentication server.
The organization or user must choose what type of EAP to use based on their requirements. EAP transfers authentication information between the user and authenticator database or server.
The EAP process works as follows:
- A user requests connection to a wireless network through an AP -- a station that transmits and receives data, sometimes known as a transceiver.
- The AP requests identification data from the user and transmits that data to an authentication server.
- The authentication server asks the AP for proof of the validity of the identification information.
- The AP obtains verification from the user and sends it back to the authentication server.
- The user is connected to the network as requested.
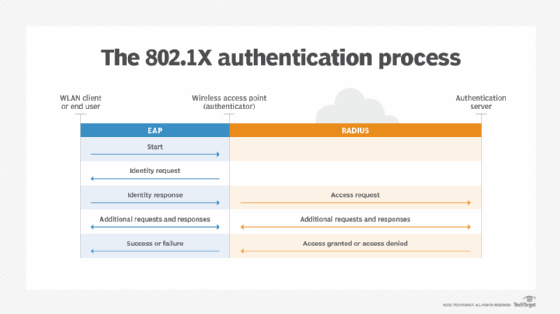
Depending on the type of EAP used, the process may vary. Below is an overview of the most common EAP methods.
Tunneled EAP methods
There are upwards of 40 EAP methods, including several commonly used ones that are often called inner methods or tunneled EAP methods. These include the following.
EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security)
EAP-TLS provides certificate-based, mutual authentication of the network and the client. Both the client and the server must have certificates to perform this authentication. EAP-TLS randomly generates session-based, user-based Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) keys. These keys secure communications between the AP and the WLAN client.
One disadvantage of EAP-TLS is the server and client side both must manage the certificates. This can be challenging for organizations with an extensive WLAN.
EAP-TTLS (Tunneled TLS)
Like EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS offers an extended security method with certificate-based mutual authentication. However, instead of both the client and the server requiring a certificate, only the server side does. EAP-TTLS enables WLANs to securely reuse legacy user authentication databases, such as Active Directory.
LEAP (Lightweight EAP)
Cisco created this proprietary EAP authentication type for mutual client and server authentication on its WLANs. The LEAP server sends the client a random challenge, and the client returns a hashed password. Once authenticated, the client asks the server for a password, and a key exchange follows.
PEAP (Protected EAP)
PEAP was created as a more secure version of LEAP. Like EAP-TTLS, PEAP authenticates clients using server-side certificates. It creates a TLS tunnel from the server to the client so the client can be authenticated through that encrypted tunnel. Unlike EAP-TTLS, with PEAP, the client must use a different EAP type.
EAP-FAST (Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling)
Cisco created EAP-FAST to replace LEAP. EAP-FAST uses a tunnel to provide mutual authentication like PEAP and EAP-TTLS. EAP-FAST does not have the server authenticate itself with a digital certificate. Instead, it uses a Protected Access Credential, which creates a one-time provisioning exchange with a shared secret, or PAC key. The PAC key handles the authentication.
EAP-SIM (Subscriber Identity Module)
This authentication type is based on the Global System for Mobile communication (GSM) SIM card used in cellphones. It uses a per-session WEP key to encrypt the data. This authentication method requires the client to enter a verification code to enable communication with the SIM. EAP-SIM 802.1X requests go through a carrier's roaming gateway to a GSM authentication server. It is used to authenticate devices that roam between commercial 802.11 hotspots and GSM networks.
EAP-MD5 (Message Digest 5)
EAP-MD5 offers a base level of support and is not recommended when implementing a WLAN. It is easier for threat actors to determine the user's or client's password with this method. It also only provides one-way authentication rather than mutual authentication, and there is no way to develop per-session WEP keys or offer a continuous rotation and distribution of WEP keys. The manual maintenance of the WEP keys can pose challenges.
The takeaway
Security is a critical aspect of public network architecture. This is more important than ever given how fast telecommunications technology is changing and the development of 5G. Security features in 5G include native support of EAP. Authentication in 5G networks is access-agnostic, so the same methods are used for 3rd Generation Partnership Project and non-3GPP access networks.
Find out about how the 3GPP specification was created for 5G security.







