intrusion prevention system (IPS)
What is an intrusion prevention system?
An intrusion prevention system (IPS) is a cybersecurity tool that examines network traffic to identify potential threats and automatically take action against them. An IPS might, for example, recognize and block malicious software or vulnerability exploits before they can move further into the network and cause damage. IPS tools continually monitor and log network activity in real time.
An intrusion prevention system expands on the capabilities of intrusion detection systems (IDSes), which are similar but less advanced tools. Unlike an IPS, an IDS can detect but not respond to malicious activity. Today, security vendors often package IPS and IDS capabilities within broader product suites or platforms.
How do intrusion prevention systems work?
An IPS tool sits inline (i.e., directly in the path of network traffic) and often behind a firewall, where it can scan and analyze incoming data that has made it inside the perimeter.
The following are three common IPS methods for recognizing threats:
- Signature-based detection. With this technique, the IPS scans for attack signatures of known network threats.
- Anomaly-based detection. Using this technique, the IPS searches for unexpected network behavior.
- Policy-based detection. This technique involves looking for activity that breaks enterprise security policies, which administrators establish in advance.
When an IPS detects threats, it may take the following actions:
- Drop suspicious network packets.
- Block suspicious traffic.
- Send alerts to security administrators.
- Reconfigure firewalls.
- Reset network connections.
IPS tools can help fend off denial-of-service (DoS) attacks; distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks; worms; viruses; and exploits, including zero-day exploits.
According to Michael Reed, formerly of Top Layer Networks (acquired by Corero), an effective intrusion prevention system should perform more complex monitoring and analysis, such as watching and responding to traffic patterns as well as individual packets.
"Detection mechanisms can include address matching, HTTP [Hypertext Transfer Protocol] string and substring matching, generic pattern matching, TCP connection analysis, packet anomaly detection, traffic anomaly detection and TCP/UDP [User Datagram Protocol] port matching," Reed said.
Types of intrusion prevention systems
Enterprises can choose from several different types of intrusion prevention systems:
- Network-based intrusion prevention system (NIPS). A NIPS scans all network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Host-based intrusion prevention system (HIPS). A HIPS has a more limited scope than a NIPS, as it resides on a single host and analyzes only traffic there.
- Wireless intrusion prevention systems (WIPS). A WIPS monitors wireless network traffic for signs of possible intrusion.
- Network behavior analysis (NBA). NBA involves analyzing network behavior for abnormal traffic flows that might indicate issues such as DDoS attacks or malware.
Benefits of intrusion prevention systems
Benefits of intrusion prevention systems include the following:
- Lowers risk of successful attacks.
- Improves network visibility.
- Provides better threat protection.
- Automatically notifies administrators of suspicious activity.
- Automates monitoring and other operational security tasks, improving efficiency and effectiveness.
Disadvantages of intrusion prevention systems
Disadvantages to intrusion prevention systems may include the following:
- IPS systems require careful tuning to minimize false positives while minimizing missed attacks.
- If an IPS system experiences a false positive, it may deny service to a legitimate user.
- If an organization does not have enough bandwidth and network capacity, an IPS tool could slow a system down.
- If there are multiple IPSes on a network, data will have to pass through each to reach the end user, causing slow network performance.
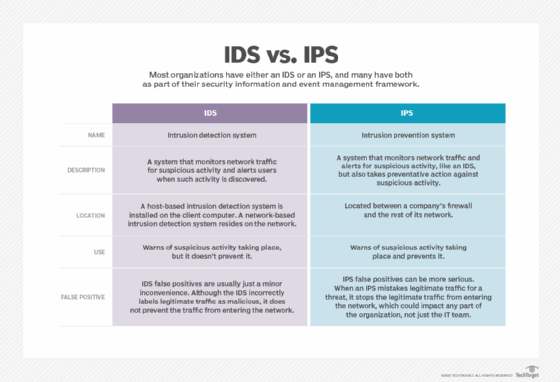
IPS vs. IDS
Like IPSes, IDSes are software tools that monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and offer greater visibility.
Unlike an IPS, however, when an IDS tool finds signs of malicious behavior, it cannot take any action on its own. Rather, if an IDS finds a threat, it alerts human administrators who must then analyze and act on the information themselves.
Once attackers gain access to a network, they may quickly move to carry out an exploit. Because IPSes can take immediate, automated action to thwart such bad actors, they have an edge on IDSes, which must wait for human intervention.








