employee onboarding and offboarding
What is employee onboarding and offboarding?
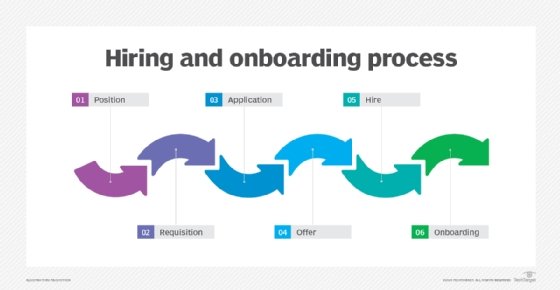
Employee onboarding involves all the steps needed to get a new employee successfully deployed and productive, while offboarding involves separating an employee from a firm.
Onboarding and offboarding in modern workplaces
Onboarding is the journey that begins when a candidate decides to join a company. It's a comprehensive process that goes beyond basic orientation; it introduces a new hire to the organizational culture, ensuring they're productive, engaged and connected.
It's a necessary component in any organization's strategy to advance employee retention, and it involves setting the foundation for the employee's entire professional journey within the company.
On the other end of the spectrum is offboarding, which starts when an employee is about to depart. Offboarding is the structured procedure to handle the transition. Whether due to retirement, career shifts or other reasons, this process safeguards organizational knowledge, ensures smooth role transition and concludes the employee's journey on a positive note.
Both onboarding and offboarding must adhere to various legal and compliance requirements, from contract management to labor laws. Ensuring that these processes comply with regulatory standards helps minimize legal risks and safeguard the organization's reputation.
This includes managing legal documents appropriately, following labor laws related to notice periods and final pay, and maintaining accurate records of all onboarding and offboarding activities.
How increased remote work impacts onboarding and offboarding
It should also be noted that the rise of remote and hybrid work models has significantly transformed onboarding and offboarding processes. Organizations have adapted to these flexible work arrangements by developing remote workflows that ensure new hires can be successfully integrated into the company culture and operations from afar.
Virtual training sessions, digital document processing and remote IT setup have become standard practices. Offboarding, too, has seen changes, with virtual exit interviews and remote retrieval of company assets ensuring that transitions are smooth, even when face-to-face interactions are limited.
Onboarding: More than just a welcome gesture
The emphasis on onboarding, whether in person or remote, has grown exponentially, reflecting its integral role in employee retention and overall organizational success. Recent studies have shown that an effective onboarding process boosts retention of new hires by more than 80%.
To further illustrate the point, consider that a mismatch between an organization's portrayal during the hiring process and the reality a new hire encounters can significantly impact morale. For instance, pitching a tech-forward work environment but initiating with outdated paper forms would be confusing and disappointing.
Integrating employees into the workplace culture efficiently, making them productive swiftly and ensuring they are aligned with company values stand out as top priorities. The use of advanced talent management software and strategies, such as assigning mentors or setting up initial manager meetings, is now the norm rather than the exception.
Offboarding: Capturing knowledge, ensuring transition
Employee offboarding and succession planning is a critical yet often overlooked phase of the employment lifecycle. It's more than just a departure process; it's an opportunity to safeguard a company's intellectual property, gain feedback for organizational improvement and maintain a positive brand image.
When conducted effectively, offboarding ensures a smooth transition with minimal disruption, allowing the departing employee to pass on vital knowledge and insights. Additionally, a well-structured offboarding process can lead to positive alumni relationships, with former employees potentially serving as brand ambassadors, collaborators or even returning talent.
An early start to offboarding, such as through mentorship programs, can make this transition smoother. In essence, thoughtful offboarding reinforces an organization's commitment to employee well-being and professionalism, even as ties are formally severed.
Additionally, data security and privacy are paramount during the offboarding process. Organizations must ensure that access rights are properly revoked, and sensitive information securely handled when an employee departs.
This includes deactivating accounts, retrieving company devices and ensuring all personal data is handled in compliance with data protection laws. A systematic approach to offboarding reduces the risk of data breaches and protects both the organization's and the employee's privacy.
Challenges of modern employee management
Over the past few decades, the talent pool has undergone significant transformations, driven in part by the evolving values and priorities of successive generations.
Baby boomers (those born between 1946 and 1964) often prioritized long-term job stability and loyalty to a single employer. Their careers were commonly marked by a linear trajectory within a singular organization or field. This dedication stemmed from a blend of post-war economic optimism, societal expectations and the allure of the lifelong benefits many companies offered.
Millennials (born between 1981 and 1996) entered the job market during the age of globalization and rapid technological change. They've exhibited a propensity to value experiences, personal growth and work-life balance over traditional job security. The economic uncertainties they faced, including the fallout from the 2008 financial crisis, coupled with an ever-connected digital world, have made them more receptive to diverse job roles, frequent career shifts and even the gig economy.
Now, as Generation Z (born between 1997 and 2012) begins to permeate the workforce, there's an even greater shift. While they've inherited the adaptability and tech-savviness of millennials, they're also demonstrating a keen sense of pragmatism, possibly shaped by growing up during times of economic and sociopolitical volatility. It's expected that the employment landscape will continue to evolve at an unprecedented pace as employers increasingly engage Gen Z employees, who grew up with digital systems and have a deep sense of purpose and desire for rapid career advancement.
Given the evolution of the workforce, it's fair to assert that employee onboarding and offboarding processes must also evolve.
For example, integrating diversity and inclusion initiatives into onboarding and offboarding processes has become vital in demonstrating an organization's commitment to an inclusive workplace. During onboarding, it's crucial to educate new hires about the company's diversity policies, cultural norms and inclusive practices.
Similarly, the offboarding process should consider and respect the diverse perspectives and experiences of departing employees, ensuring that feedback mechanisms are in place to learn from their unique insights and improve inclusivity continuously, with HR leading the charge.
HR: The orchestrator of seamless transitions
For both onboarding and offboarding, the HR department stands at the nexus, ensuring synchronization among all involved parties. From IT ensuring timely system access (or its retraction) to administrative departments handling logistics, HR ensures everyone moves in harmony.
Both processes can be complex and resource intensive, and talent management is far more dynamic in nature than in previous generations. To ease the burden, contemporary HR technology now offers dedicated modules for these processes, providing tailored solutions for the modern challenges of onboarding and offboarding.
HR software streamlines and automates these multifaceted procedures, ensuring consistency, efficiency and thoroughness. Onboarding modules often encompass digital orientations, training schedules and documentation handling, offering new hires a seamless initiation into the company.
For remote employees, cloud-based HR platforms allow for seamless access to onboarding materials and training programs from anywhere, fostering a flexible learning environment. E-signature tools have eliminated the need for physical paperwork, speeding up the contract signing and policy acknowledgment processes.
Employee self-service portals empower individuals to manage their personal information, benefits and compliance documents, fostering a sense of autonomy and engagement from day one.
Offboarding functionalities ensure a structured exit, from capturing feedback through exit interviews to overseeing the return of company assets. When done well, these practices provide insights into the employee's experience, identifying strengths and areas for improvement in the onboarding and offboarding workflows.
This continuous feedback loop enables HR teams to enhance the overall employee journey, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and responsiveness to employee needs.
Additionally, centralizing the complex processes of onboarding and offboarding with HR software can enhance the employee experience and ensure that organizations capture critical data, maintain compliance and optimize their talent management strategies.
Looking forward, the use of AI and machine learning is expected to dramatically alter the onboarding and offboarding experience, automate routine tasks and personalize the process to align with individual business needs and preferences.
New employees have specific needs during the various phases of onboarding, from pre-onboarding to their first months on the job. Use this checklist to welcome -- and retain -- them.





